Monetory Policy and its instruments
Monetory Policy is a policy adopted by the authorities of a country to cater with the financial stability of the country.
Definition : Monetory policy consists of management of money supply and interest rates, aimed at achieving macroeconomic objectives such as controlling inflation, consumption, growth, and liquidity.
Monetory Policy are of two types ; Indirect and Direct Instruments.
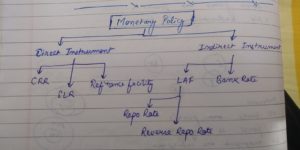
Direct Instruments :
1. CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) – CRR is the amount of funds that the banks have to keep with the RBI. At present the current CRR is 3%.
2. SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio) – The share of net demand and time liabilities (NDTL) that the banks must maintain in safe and liquid assets such as government securities, cash and gold. Current SLR ratio is – 18.0%
3. Refinance Facilities – Sector Specific Refinance facilities provided to banks.
Indirect Instruments;
1. LAF – (Liquidity Adjustment Facility)
2 types of LAF;
Repo rate : Repurchase Offer Rate Rate at which banks borrow rupees from RBI. Current repo rate is 4.4%.
Reverse Repo rate : Reverse Repurchase Offer Rate , Rate at which RBI borrows money from commercial banks. Presently the Reverse Repurchase Offer Rate is 3.75%
2. Bank Rate -It’s the rate at which the RBI is ready to purchase or rediscount invoices of exchange or other commercial papers. The bank rate is available under Section 49 of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. The rate is associated with the MSF rate and changes automatically as and when the MSF rate changes along with the policy repo rate changes.
Rate at which RBI provides medium to long term loans to commercial banks and also give discount on them.
Marginal Standing Facility : MSF – A facility under which planned commercial banks can lend extra amount of immediate cash from the RBI by dipping into their Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) collection up till a limit at a penal rate of interest. This, in turn, provides a safety valve against unexpected liquidity shocks to the banking system.
MSF can also be defined as interest rate offered by RBI to all commercial banks for overnight period. This facility is given to maintain the Liquidity stock of the Bank. It is always higher than repo rate.
MSF = Repo rate + 1%
At present MSF = 4.65%
Current rates;
CRR – 3%. SLR – 18.0%. Repo rate – 4.4%. Policy Repo rate – 5.15%. Reverse Repo rate – 3.75%. Bank Rate – 4.65%. MSF Rate – 4.65%
Visit the link for detailed list of all rates https://m.rbi.org.in//home.aspx
Follow the link for detailed explanation on Monetory Policy and information;
https://cleartax.in/s/monetary-policy-of-india-rbi
Visit the link below to read difference between MSF and repo rate. Also you can see the effect of these rates on a common person ;https://www.bankbazaar.com/finance-tools/emi-calculator/repo-rate-vs-msf.html