Lower Critical Temperature
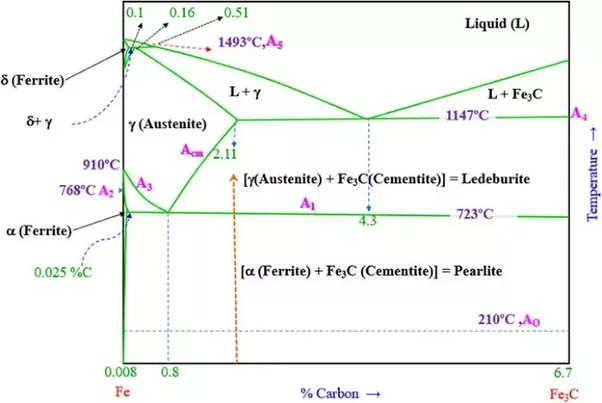
All Steel being heated at a uniform rate from room temperature show a comparatively much slow rise in temperature on reaching a temperature about 723 deg. Celsius. This temperature at which a check or arrest in rise of temperature appears in Steel at uniform rate of heating is called Lower Critical Temperature. This temperature has the same value with all carbon steel.
At this temperature structural changes starts in steel. Its Pearlite and Ferrite or Pearlite and Cementite start changing into Austenite (subject to carbon content)
Austenite is a solid solution of carbon in Gamma iron. As long as this change is continued the rise of temperature is slow, despite uniform rate of heating throughout.
Upper Critical Temperature
Steel on further heating at an earlier rate of heating even after reaching Lower Critical temp. continue showing a slughish rise in temp. until all structural changes to form austenite are complete. The completion of formation of Austenite happens on reaching a particular temp. This temp is termed as Upper Critical temp.
The temp. at which the check or arrest in rise of temp. of steel during heating from room temp is over is known as Upper Critical temp.
The value of this temp. is different for different carbon percentages in Steel. After upper critical temp the rise in temp is restored to the initial rate as it has been from room temp. to Lower Critical temp.